All solar power systems work on the same basic principles. Solar panels first convert solar energy or sunlight into DC power using what is known as the photovoltaic (PV) effect. The DC power can then be stored in a battery or converted by a solar inverter into AC power which can be used to run home appliances. Depending on the type of system, excess solar energy can either be fed into the electricity grid for credits, or stored in a variety of different battery storage systems.
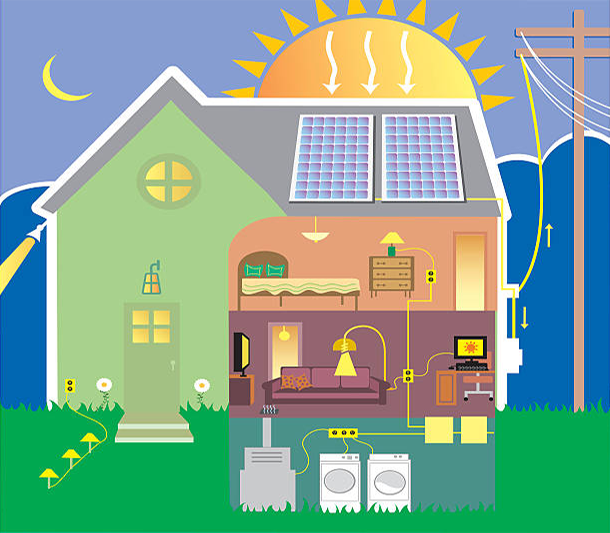
(Image: Gettyimages)
Following are three main types of solar power systems available in the market for investors to opt for:
On-grid - also known as a grid-tie or grid-feed solar system
Off-grid - also known as a stand-alone power system (SAPS)
Hybrid - grid-connected solar system with battery storage
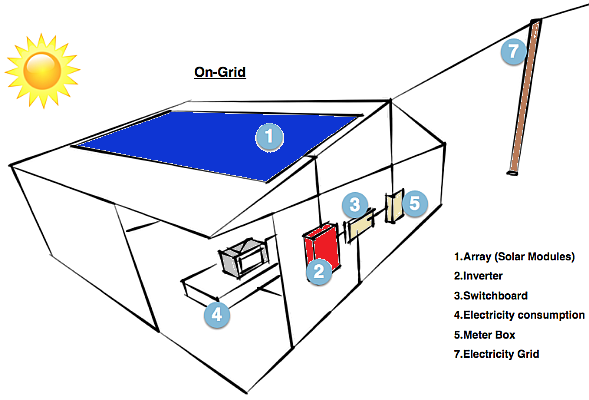
On-grid Solar System
On-grid solar installations are currently the most common and most affordable type of system. These systems use a simple solar inverter to convert DC power from solar panels to AC power, which can be fed directly into the grid or used in your appliances. They are best suited for urban areas with strong grid connectivity.
(Image: CER)
Any excess power generated in the process is transferred to the utility grid and the customers get a credit for the amount of energy exported. The practice is also known as net metering. Through net metering, an on-grid connection assists you in earning a faster return on investment (ROI), lower electricity overheads, and savings.
However, if you live in a rural area, it can be expensive to install the power lines or poles that link your system with the grid. What’s worse, in case of a power shutdown, your solar system will turn off if it is not tied to a battery backup system, leaving you without energy. Due to safety reasons, the on-grid system cannot function electricity during a blackout. So, if the solar panel system is generating electricity to the faulty grid, it will risk people’s s safety.
On-grid Solar System
Main Components
Solar panels + Grid + Grid-tied inverter + Meters
Features
Large utility-scale model、Surplus supply to the grid
Night power is drawn from the grid
Applicability
Best suited for Urban Areas with Strong Grid Connectivity
Pros
Faster ROI、Better savings
Constant Reliable Power、Accessible grid power backup
Cons
Can be costly to source equipment
Performance is tied to the grid
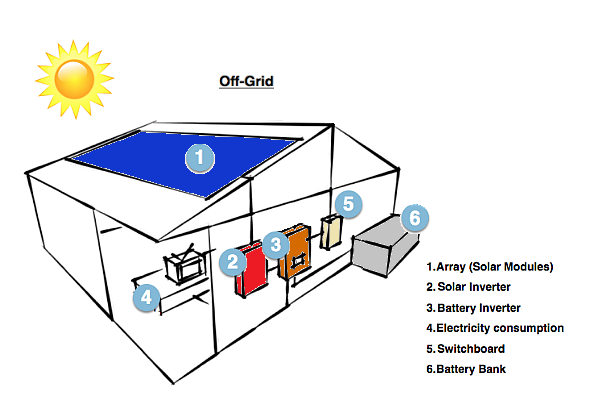
Off-grid Solar System
Well-known as standalone systems, off-grid solar systems help you in building a self-reliant powerhouse on your premises. Here, the MPPT(Maximum Power Point Tracker) helps the PV array to charge the battery bank, then transfer it to the inverter. The cost of inverters and off solar grid systems makes it expensive and commonly required by people far away from remote or public electricity grid stations.
(Image: CER )
When going off-grid, you are no longer dependent on electricity power company’s policies and terms. At the same time, you no longer depend on giving monthly bills anymore. Moreover, no grid connection means freeing yourself from the risk of power outages or fluctuating power costs. Also, it can be the most eco-friendly and sustainable home energy storage system. Without the grid, you can minimize your carbon footprint.
Of course, going off-grid requires adequate battery storage and inverters, representing higher initial costs. Significantly, off-grid solar systems must be designed appropriately so that they will generate enough power throughout the year and have the adequate battery capacity to meet the home’s power demands, even on snowy or rainy days. Hence, you must use power sparingly. You’ll have to tightly monitor your energy usage and lifestyle, such as using most of your power in the daytime or tightly restricting night-time expenses.
Off-grid Solar System
Main Components
Solar panels +Battery Systems+Inverter
Features
Completely independent、Long life、Hassle free
Applicability
Home or Office、Micro-grids、Rural Areas
Agricultural Sector、Construction Sites
Pros
Independence、No more blackout、No electricity bills
High return on investment
Cons
Can be costly to replace equipment、Limited storage
Power usage must be strategized
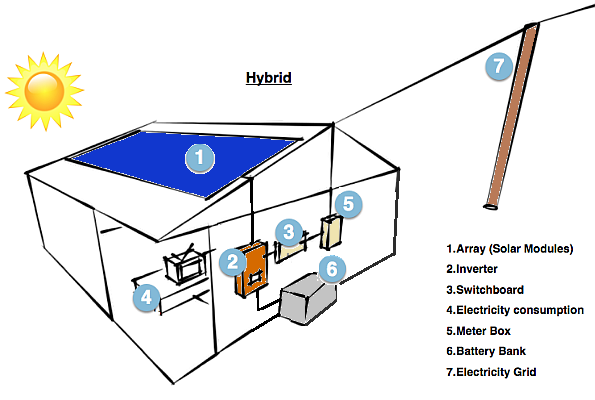
Hybrid Solar System
A hybrid solar system is grid-tied with battery storage and a special “smart” inverter. Here, the extra energy produced by the solar system after the energy consumption by appliances is transferred to the battery bank. Once the batteries are completely charged, they can export the extra energy to the grid. Hybrid solar systems are usually the best choice for residential properties.
(Image: CER )
While hybrid setups are grid-tied, they come with solar battery storage, which means you can maximize the consumption of the power generated from the panels. Hybrid systems can provide the flexibility of being able to store the energy you generate during the day instead of feeding it back into the grid - typically at a low feed-in tariff. This energy can then be used in the evening instead of buying power back at a higher price. In general, they combine the best of three worlds: the convenience of a grid-connected system, the credits through the Net Metering, and the security of a battery backup.
There’s a lot to install upfront, making the initial investment bigger. While you can budget for a smaller battery bank than with an off-grid setup, the cost still needs some thought. Also, some specialized equipment, such as a smart hybrid inverter, adds to the price tag. Here, lots of space might be necessary for the required parts.
Hybrid Solar System
Main
Components
Solar panels + Battery Systems + Hybrid Inverter + Meters
Features
Night power from a battery
Surplus supply to the grid
No blackouts ever
Applicability
Home or Office、Micro-grids、Rural Areas、Agricultural Sector
Pros
Feed-in tariffs、Continuous power supply、High return on investment
Cons
Bigger initial investment、Cover lots of space
Conclusion
Any of the above-mentioned systems can be suitable for the consumers, depending on their specific requirements and budget. You’ll need to weigh many factors: How far do you live from the national grid? What’s your home coverage and typical energy consumption? How much initial investment are affordable? It’s sophisticated while you’re building your dream home. Maybe you can turn to some solar experts who can help you navigate all the issues involved.
Overall, all system designs will give you significant solar benefits, like saving your monthly bills and diminishing your carbon footprint.